Overview: Defence Sector
Lately, a noticeable transformation has taken place in the worldwide defence arena. We’ve transitioned from a period where a single influential power held dominance (called ‘Unipolarity’) to a more evenly distributed and diverse situation (‘Multipolarity’). This shift has been instigated by the ascent of robust Asian nations challenging the conventional Western powerhouses on multiple fronts. These challenges encompass not only their economic expansion but also their military capabilities.
In the year 2022, a striking upswing in military expenditures was observed across the globe, reaching an unprecedented peak as per SIPRI’s records. The global military spending witnessed a 3.7% real term increase when adjusted for inflation, culminating in a substantial $2,240 billion expenditure, equivalent to roughly 2.2% of the global GDP.
Global Trends: Military Expenditure:
| Country | Military Expenditure (2022) | % of Total World Military Expenditure | % share of GDP | Change from the Previous Year | Additional Notes |
| United States | $877 billion | 39.1% | 3.5% | 0.7% | Includes military aid to Ukraine. |
| China | $292 billion | 13.0% | 1.6%* | 4.2% | Continued growth for the 28th consecutive year. |
| Russia | $86.4 billion | 3.8% | 4.1%* | 9.2% | — |
| India | $81.4 billion | 3.6% | 2.4% | 6.0% | Fourth largest spender globally; significant increase. |
| Saudi Arabia | $75 billion | 3.3% | 7.4%* | 16.0% | Part of the top five spenders, totaling 63% of global spend. |
| United Kingdom | $68.5 billion | 3.1% | 2.2% | 3.7% | — |
| Germany | $55.8 billion | 2.5% | 1.4% | 2.3% | — |
| France | $53.6 billion | 2.4% | 1.9% | 0.6% | — |
| South Korea | $46.4 billion | 2.1% | 2.7% | -2.5% | — |
| Japan | $46 billion | 2.1% | 1.1% | 5.9% | — |
Source: SIPRI, Fisdom Research, *Number are estimates.
India’s position as a top-five global military spender highlights its strong defense commitment, yet a substantial gap persists compared to the United States and China, with the former investing approximately 11 times and the latter around four times more. Although India contributes 3.6% to global defense spending, the combined contributions of the US and China exceed 50%, underscoring the need for India to strategically narrow this disparity. Achieving this demands resource allocation, efficient utilization, and potential collaborations to bolster defense capabilities while maintaining a balance with other national priorities. Embracing technological advancements and gradual, sustainable growth in defense spending is crucial for India’s global security role and its dedication to international stability.
Tailwinds: Propelling India’s Defense Industry Advancement
1. Defense Budget: Prioritizing Modernization and Growth
The FY24 Union Budget outlines a comprehensive expenditure plan amounting to Rs 45 trillion. Within this framework, the Ministry of Defence has been allocated a budget of Rs 5.9 trillion, constituting 13% of the total budget. This allocation encompasses Rs 1.4 trillion specifically designated for defense pensions. In comparison to the budget of the preceding year, the aggregate defense budget has risen by Rs 683 billion, denoting a growth rate of 13%.
In the budget, particular emphasis has been placed on the modernization and enhancement of the defense services’ infrastructure. To facilitate this objective, capital allotments have been raised to Rs 1.6 trillion, reflecting an increment of Rs 102 billion from the previous year, indicative of a growth rate of 6.7%. This augmented investment seeks to elevate the capabilities and preparedness of our defence forces for upcoming challenges.
| Particulars | FY23RE | FY24BE |
| Defence Capital Budget | ₹ 1,50,000 | ₹ 1,62,600 |
| Y-o-Y growth | 8.2% | 6.8% |
| Defence Pensions | ₹ 1,53,400 | ₹ 1,38,205 |
| Y-o-Y growth | 31.2% | 15.5% |
| Defence Servies (Revenue expenditure) | ₹ 2,59,500 | ₹ 2,70,120 |
| Y-o-Y growth | 13.0% | 15.9% |
| Total Defence Budget | ₹ 5,62,900 | ₹ 5,70,925 |
| Y-o-Y growth | 16.0% | 13.1% |
| Capital as % of Total Budget | 26.6% | 28.5% |
| MoD (Civil) | ₹ 20,100 | ₹ 22,613 |
| MoD Budget | ₹ 5,83,000 | ₹ 5,93,538 |
| Particulars | Revenue Exp | Capital Exp | Total |
| Pension | ₹ 1,38,200 | — | ₹ 1,38,200 |
| Defence Services | ₹ 2,70,100 | ₹ 1,62,600 | ₹ 4,32,700 |
| MoD (Civil) | ₹ 13,800 | ₹ 8,800 | ₹ 22,600 |
| Total | ₹ 4,22,100 | ₹ 1,71,400 | ₹ 5,93,500 |
Source: Budget Documents, Fisdom Research. Amount in crores
Challenges:
- India’s defence spending has been on a consistent rise, with recent growth predominantly attributed to higher pension costs arising from the One Rank One Pension (OROP) scheme and increased salaries based on the recommendations of the 7th Pay Commission.
- As a result, a noteworthy escalation in defence revenue expenditure has occurred, indicating a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 12% from FY14-19. However, the defence capital expenditure (capex) growth has been more moderate, exhibiting a CAGR of 4%.
- Alarmingly, the proportion of defence capex within the overall defence expenditure hit a multi-year low of 24% in FY19, hinting at potential adverse effects on the modernization and infrastructural progress of India’s defence sector prior to FY20.
Key Strategies for Problem Resolution
- Defense capital expenditure (capex) has demonstrated robust growth with a 12.5% Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) from FY19 to FY23, reflecting increased investments in modernization and infrastructure enhancement.
- The introduction of the One Rank One Pension (OROP) and recommendations from the Pay Commission paved the way for a higher allocation in the capital expenditure budget, bolstering the capabilities of India’s defense industry.
- Despite challenges such as reduced recruitment due to the pandemic, the incorporation of advanced platforms like submarines, fighter aircraft, communication systems, helicopters, and armoured vehicles has contributed positively to the defence industry’s expansion.
- Furthermore, favourable policy initiatives like the Agnipath Scheme are anticipated to elevate defence capex in the upcoming years further, fostering substantial investments in the sector.
We expect that even a tiny redirection from the budget allocated to personnel and pensions could provide significant headroom for allocation in defence modernization efforts.
2. Surging Momentum in Export Expansion
In a span of just four years, from FY15 to FY19, India’s defence exports have witnessed a remarkable growth of 5.5 times. This exponential expansion owes its momentum to a strategic blend of governmental reforms and initiatives to enhance the ease of doing business. Fuelled by a vast pool of skilled professionals, the nation’s competitive edge in terms of cost advantage positions it as an appealing hub for global Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) to manufacture and export defence products.
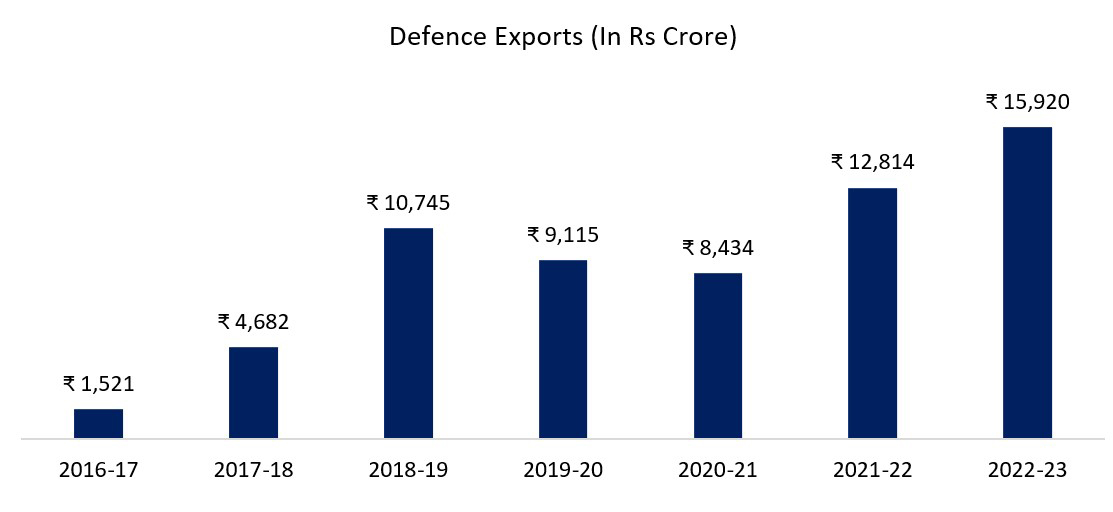
Source: Ministry of Defence, Fisdom Research
Collaborative partnerships with renowned international OEMs have enabled India to harness the benefits of reduced costs, facilitating substantial defence exports to various countries, including Italy, Maldives, Sri Lanka, Russia, France, and more. This burgeoning trend not only propels the Indian defence industry but also solidifies the nation’s stature as a formidable contender within the competitive arena of the global defence market.
Here is a compilation of selected listed and unlisted entities that have received the Government of India’s approval for exporting goods
| Class of equipment | No of items | Producing Company |
| Aeronautical systems | 19 | Hindustan Aeronautics |
| Centre for Airborne Systems | ||
| Larsen and Toubro | ||
| Bharat Electronics, Data Patterns, | ||
| Alpha Design Technologies | ||
| Armament and combat systems | 41 | Ordnance Factory Board |
| Economics Explosives, Tata group | ||
| Larsen and Toubro, Ordnance Factory | ||
| Bharat Forge | ||
| BEML | ||
| Tata group of companies | ||
| Bharat Electronics, Dynalog, Theta | ||
| Tech Robotics | ||
| Electronics and communication systems | 27 | Bharat Electronics |
| Life protection systems | 10 | MKU, ATAMASTCO |
| Micro-electronics devices and computational systems | 4 | Bharat Electronics |
| Missile systems | 4 | Bharat Dynamics, Bharat Electronics |
| Brahmos Aerospace | ||
| Bharat Dynamics | ||
| Bharat Electronics, Bharat Dynamics | ||
| Naval systems | 28 | Bharat Electronics |
| NBC | 16 | Permionics Membranes |
| Materials | 7 | Jindal Stainless |
Source: Company financials, Philip capital, Fisdom Research
Initiatives undertaken by the government of India to boost exports:
- The inception of the Scheme for Promotion of Defence Exports has facilitated aspiring exporters to secure Government of India certification for their products, enabling access to testing infrastructure and field trials.
- Defence Attaches stationed abroad are provided with financial backing to advocate for the export of India-manufactured defence products from both the public and private sectors.
- The indigenous aircraft carrier LCA Tejas has garnered a favourable reception overseas, exemplified by the Malaysian Air Force’s consideration of a prospective order for 36 Tejas jets, projecting an export potential of approximately Rs 111 billion.
- India has extended an offer to establish production facilities for manufacturing light combat aircraft (LCA) and helicopters in Egypt, capitalizing on export opportunities within the Middle East and North Africa region.
- Elevated dialogues with friendly nations, including Egypt, Argentina, Indonesia, and Malaysia have unfolded, potentially paving the way for forthcoming orders from Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- Governments are collaborating to promote indigenous products in the defence sector.
- DPSUs and OFB will be required to generate at least 25% of their revenue from exports.
- The export clearance process is streamlined and time-bound, ensuring smooth operations.
- The target for defence exports sales is set at Rs 350 billion by FY25
- India benefits from cost advantages and global partnerships, driving its defence exports.
- The government provides financial support to Defence Attaches for promoting defence exports.
- India’s defence industry is making significant strides in exporting weapon systems.